library(pacman)
p_load(ggplot2)Using ggplot
Introduction to ggplot2
ggplot2 is a popular package in R for creating more advanced and beautiful data visualizations. It allows you to build complex plots by adding layers one by one, making it flexible and powerful. Let’s walk through the basics of using ggplot2.
Installation and Loading
First, you need to load the ggplot2 package. If you haven’t installed it yet, you can do so with install.packages("ggplot2").
Building a Plot with ggplot2
Creating a plot with ggplot2 involves a few simple steps:
- Prepare Your Data: Make sure your data is in a data frame.
- Create a ggplot Object: This is like setting up your canvas.
- Add Layers: These layers define how your data will be displayed (e.g., points, lines, bars).
- Customize: Add titles, labels, and customize the appearance.
Let’s go through each step in more detail.
Prepare Your Data
Your data should be in a data frame. Here’s an example data frame:
my_data <- data.frame(
x = c(1, 2, 3, 4, 5),
y = c(10, 15, 13, 17, 20)
)Create a ggplot Object
This is where you start building your plot. You specify your data and how the variables map to the plot’s axes.
ggplot(data = my_data, aes(x = x, y = y))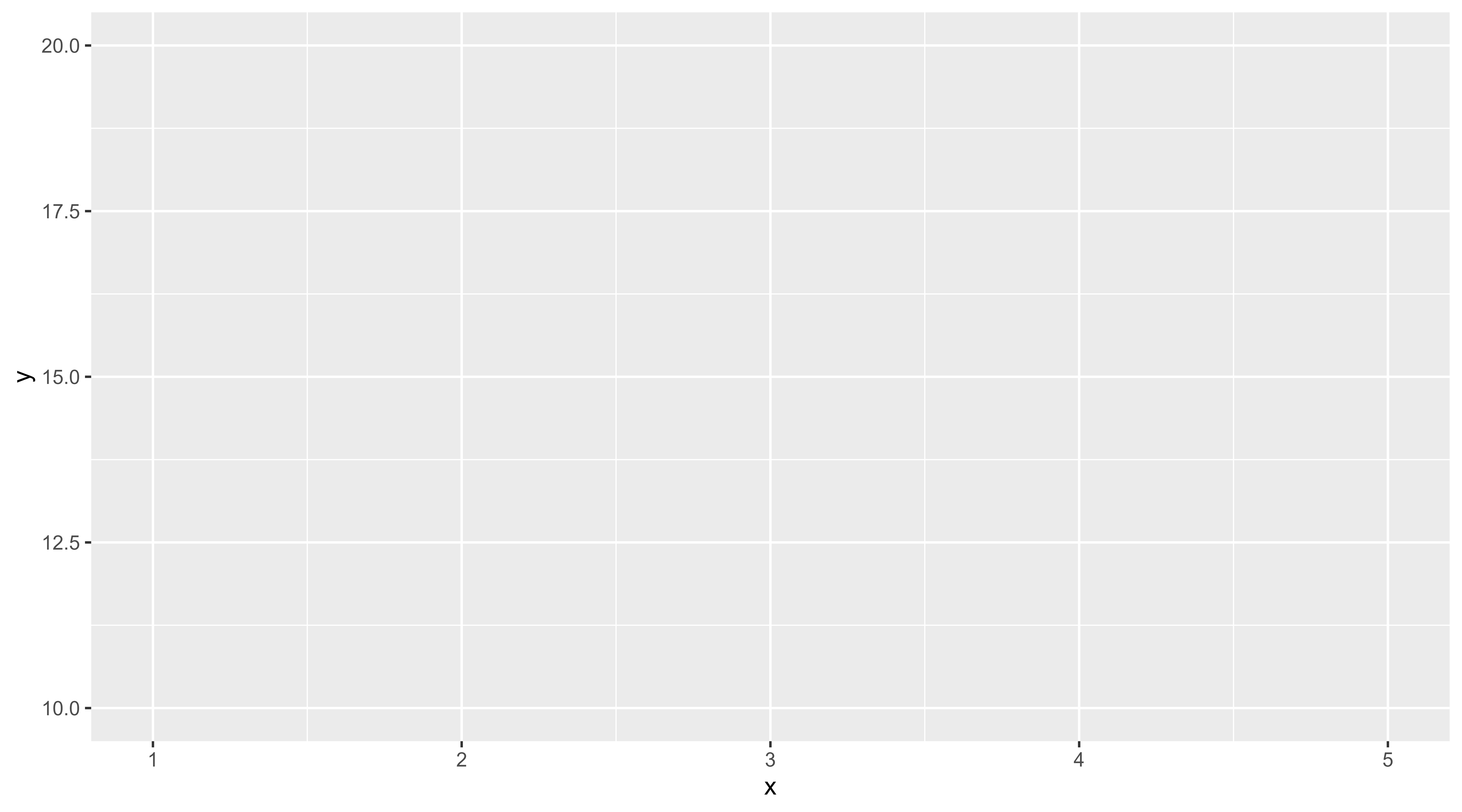
Add Layers
Layers define what kind of plot you want. For a scatter plot, you use geom_point().
ggplot(data = my_data, aes(x = x, y = y)) +
geom_point()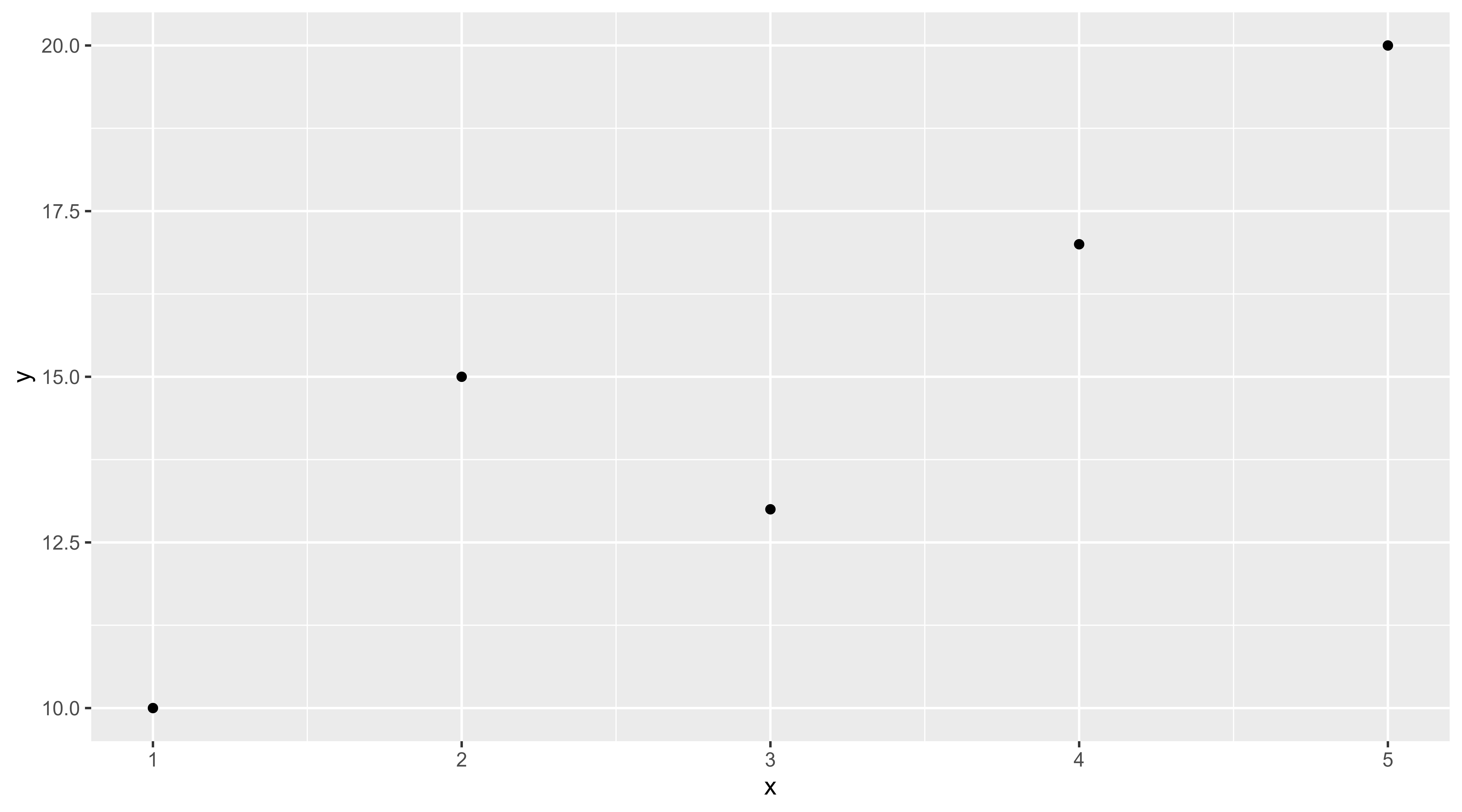
Customize Your Plot
You can add titles, labels, and more to make your plot look better.
ggplot(data = my_data, aes(x = x, y = y)) +
geom_point() +
labs(title = "My Scatter Plot", x = "X Axis", y = "Y Axis")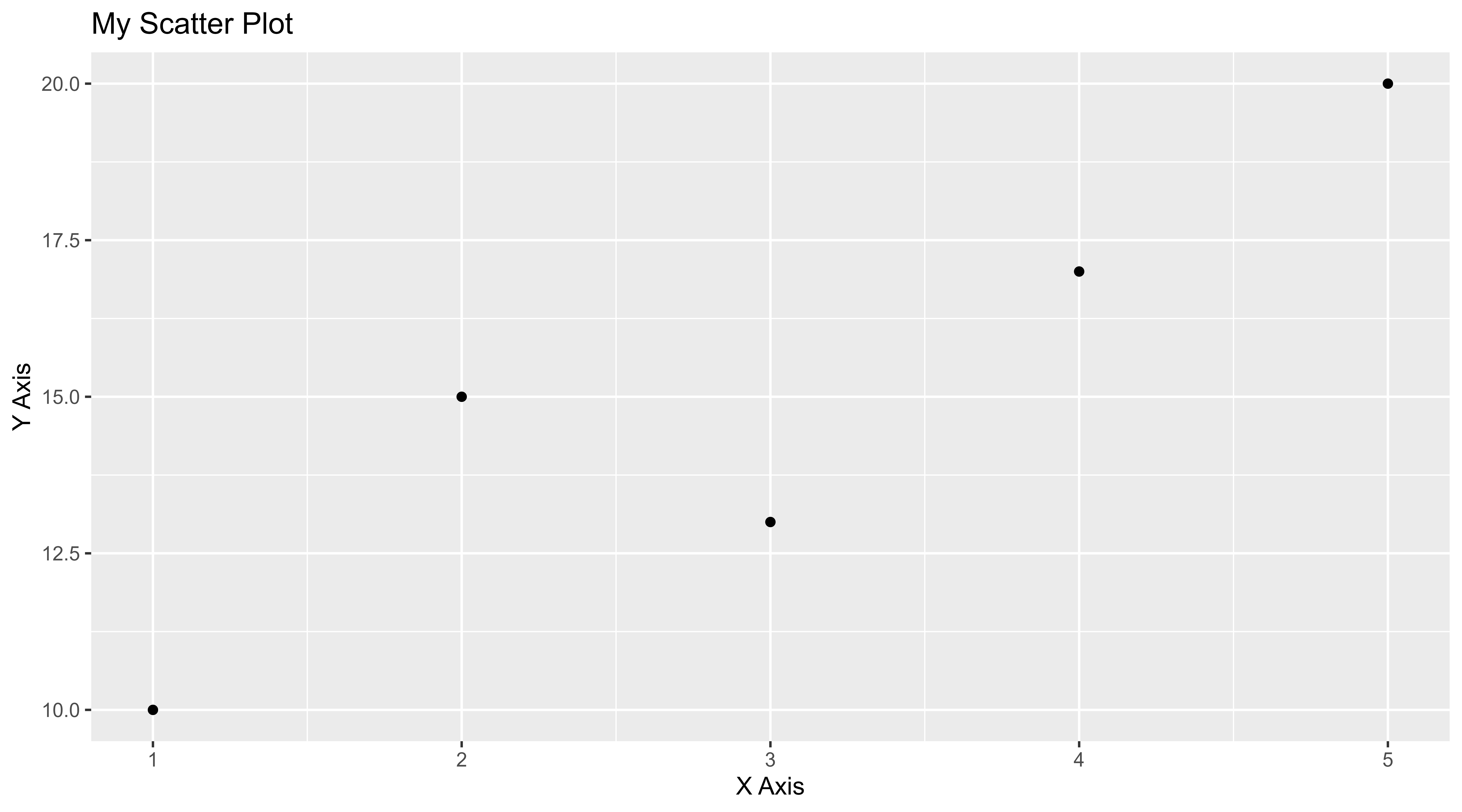
Example
Now, let’s put it all together with a real example. We’ll use WEO data from 1980 onwards in the USA to create a scatter plot.
# Load other necessary packages
library(dplyr)
library(haven)
library(here)
# Read WEO data
weo <- read_dta(here("databases/WEOApr2023Pub.dta"))
weo_us <- weo %>%
select(ifscode, year, lur, pcpi_pch) %>%
filter(ifscode == 111)
#Filtering to only include 1980 data onwards
weo_us <- subset(weo_us, year >= 1980)
# Create a ggplot object with data and aesthetics
gg <- ggplot(data = weo_us, aes(x = lur, y = pcpi_pch))
# Add a scatter plot layer
gg <- gg + geom_point()
# Customize the plot labels
gg <- gg + labs(title = "United States: Unemployment and Inflation",
x = "Unemployment (percent)", y = "Inflation (percent)")
# Render the plot
gg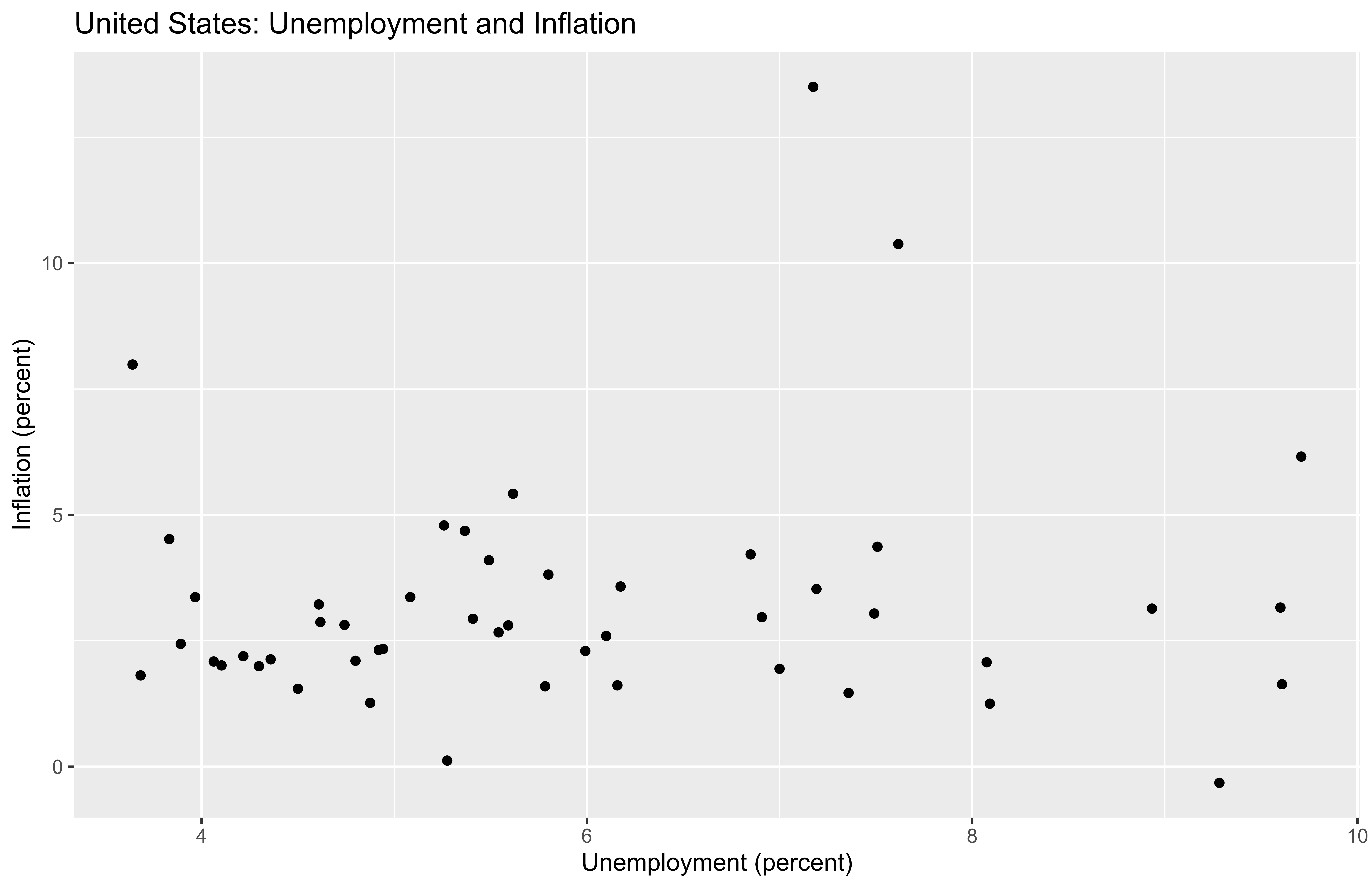
Or, you can combine all steps into a single command:
gg <- ggplot(data = weo_us, aes(x = lur, y = pcpi_pch)) +
geom_point() +
labs(title = "United States: Unemployment and Inflation",
x = "Unemployment (percent)", y = "Inflation (percent)")
gg
This chart does not look very pretty yet. We will fix that later when we use themes.